Creating a Workspace
In this section, you will learn how to create a new workspaces in the platform. In addition, you will also get to know how to navigate the interface of a new workspace.
The process of creating a workspace consists of the following:
- Setting up the initial information
- Configuring category and code
- Setting up dynamic files
- Adding static files
- Configuring models
Setting Up Workspace Info
First, let's set up a workspace information: workspace name, privacy thumbnail enabling you and other users in the organization to visually identify a workspace.
To set up workspace info, do the following:
-
Login to the platform.
-
In the right-hand panel, click the Collaborate module, and then click the Workspaces tile.
The Workspaces Dashboard page displays all the existing workspaces.

-
In the Workspaces Dashboard page, click the Create New Workspace tile.
The Create New Workspace dialog box is displayed.
-
In the Create New Workspace dialog box, do the following:
-
Type the workspace name in the Workspace Name field.
-
Select one of the following workspace privacy options in the Workspace Privacy section:
Workspace Privacy Description Workspace Visibility Public A workspace that is open to all the users in the organization All users can view and edit this workspace Private A workspace that is open for only you. Only you can view and edit this workspace Close Group A workspace that is open to only team members selected in the group All users in the group can view and edit this workspace -
Upload an image or simply drag-n-drop an image that you want to display as the workspace thumbnail in the Thumbnail section.

-
-
Do one of the following:
-
Click the Save button to save and exit.
-
Click the Next button to go to the next screen.
-
Setting Up Dynamic Files Filters
Search, select, and allow dynamic addition of layers and categories (that meet pre-defined criteria) in the workspace.
For example, suppose you create a new AOI on the map and populate it with SAR image layers. When you apply a dynamic files filter, the workspace automatically adds any new SAR images uploaded to the application that match the AOI. This way, your AOI always stays updated with the latest SAR images—without requiring you to add them manually.
To set up dynamic file filters, do the following:
-
Click the Create New Filter button and do the following:
-
Click the Source Data Type drop-down list and select the data type that you want to enable in the workspace.
-
Click the Categories drop-down list to select type of categories that can be enabled in the workspace. Furthermore, you can click the > icon to open a specific category to view and add a sub-category. For example, click the aircraft category to open, view, and add sub-categories namely B52, F16, F35, MIG 31, and so on…
-
Select the Start Acquisition Date and End Acquisition Date of the images that you want to dynamically filter onto the Area of Interest (AOI).
-
Click the Draw An Area of Interest (AOI) button to draw a specify a geographic extent on the map. Once an area of interest is specified, all the current and future images of this specified area will be automatically made available to you.

-
-
Do one of the following:
-
Click the Save button to save and exit.
-
Click the Next button to go to the next screen.
-
Adding Static Files to the Workspace
Add single or multiple files of the same or different formats from the images library to the workspace.
To add static files, do the following:
-
Click the Filter icon, and do the following:
- Type the keyword in the Search field to find an appropriate static file. For example, Palm Tree.
- Select a Start Acquisition Date and End Acquisition Date of the static images.
- Select the type of source file you want to add as static files in Source Data Type drop-down list.
- Click the Draw an Area of Interest button to specify an area of the static files.

-
Do one of the following:
- Click the Save button to save and exit.
- Click the Next button to go to the next screen.
If you are new to using the platform, you might not see any images in the static file list tab because you may not not uploaded multiple images to the platform yet.
Dynamic files are like temporary files that can be added or removed as needed. You can draw an Area of Interest (AOI) and specify which types of files (formats, category, sub-category) should be included. If any user in your organization uploads matching files, they will be automatically added to the AOI.
Static files, on the other hand, are permanent files. Once uploaded to the library, these files can be searched and reused across any workspace you choose.
Configuring Auto-Run Models
Select AI Models that you want to automatically run in this workspace.
To configure auto-run models, do the following:
-
Type a keyword in the Search field to find an AI model. For example, Palm Tree.
-
Select the AI model and turn on the toggle button to run it automatically. This enables the platform to automatically run the selected AI model on any of the files or layers added dynamically or manually to the workspace, thereby detecting the objects that the AI model is designed to detect.
-
Click the Create button to create a new workspace.

Navigating a New Workspace Page
In this section, discover how you can navigate a new workspace page module.
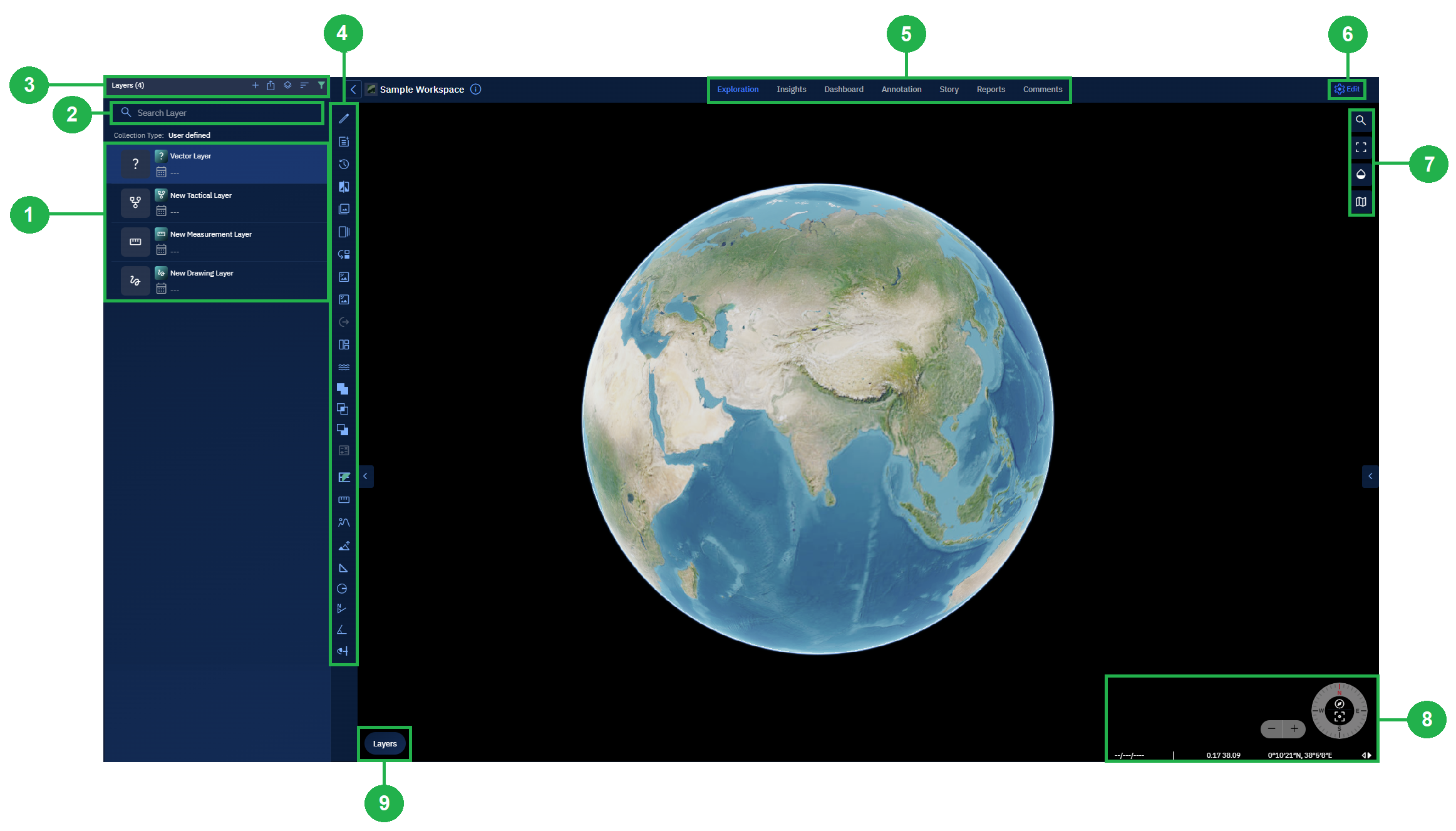
The Workspace interface enables you to do a host of tasks and actions namely view all types of layers, search layers, add new layers/collections, edit workspaces, and so on...
| # | Element | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Layers List | View existing layers and any layers you add to the workspace in this section. |
| 2 | Search Layer | Quickly find a specific layer by name using the search bar. As you type, matching layers are dynamically filtered from the Layers List, making it easy to locate layers in workspaces with large datasets. |
| 3 | Layers Ribbon | Add new layers such as Drawing or Vector layers to the workspace. Includes features like toggling footprint visibility, sorting layers, and filtering them. |
| 4 | Analyst Tools | Execute spatial analysis tasks like comparing vector layers, image comparisons, ground length measurements, and more. |
| 5 | Workspace Tabs | Visualize and analyze datasets through modules such as Explore, Insights, Dashboard, Annotation, and Story. Each module supports different aspects of geospatial analysis. Common functionality is available in both the Explore module and Workspace page. |
| 6 | Edit Workspace | Modify workspace settings like its name, visibility (public/private), and dynamic filters. This is only available within the Workspace page. |
| 7 | Workspace Map Options | Navigate and control how the map is displayed. Jump to specific coordinates, switch to full-screen, adjust map transparency, or toggle map views. Common to both Explore module and Workspace page. |
| 8 | Azimuth & Lat-Long | Switch between Lat-Long and MGRS formats, zoom in/out, or reset azimuth for true north. Common to both Explore module and Workspace page. |
| 9 | Base Map Layers | Select or switch base maps for geographic reference. Overlay one or more data layers and choose a height map. Common to both Explore module and Workspace page. |